Stokes equation
Stokes' equation is a good place to see the formulation and the assembly of various blocks in the system. As in the Poisson sample, it is optionnally solved as a non-linear problem.
The finite element type for the hydrostatic pressure P is given by degreeP. When positive, it uses a discontinuous finite element P0 or P1D. When negative, it uses a lagrange finite element with a degree equal to degreeU+degreeP. Hence degreeU=2 and degreeP=-1 means lagrange degree 2 for U and lagrange degree 1 for P.
/*
* nvi_Stokes__form__grid2.cpp
*
* 2D / cavity / stationnaire
*
*/
#include "nvi_Stokes.h"
#include "nvi_Formulation__framework_01.h"
#include "navlib_math_flt.h"
#include <iostream>
namespace nvi::FormulationFrameworks
{
struct UProblem__Stokes__0 : public Formulation__framework_01
{
struct parameters_t
{
bool newton = false;
uint degreeU = 1;
int degreeP = 0;
Expr nu = 1.;
};
UProblem__Stokes__0(Processor& proc, txt name, Mesh&& m, const parameters_t& pp) : Formulation__framework_01(proc,name,std::move(m))
{
auto U = variable("U",2,pp.degreeU);
auto P = variable("P", pp.degreeP);
auto U_ = dual(U);
auto P_ = dual(P);
auto points = _points_ ();
auto dx = _dx_();
auto x = X (points);
auto u = U (points);
auto p = P (points);
auto u_ = U_(points);
auto p_ = P_(points);
auto grad_u = grad(U) (points);
auto grad_p = grad(P) (points);
auto grad_u_ = grad(U_)(points);
auto div_u = trace(grad_u);
const double pi = std::acos(-1.);
const auto nu = scalar_of_X(pp.nu,x);
auto I = identity_matrix();
auto _I_ = Tensor::_I_(dim);
if (pp.newton)
{
auto formU = form1( dx * (nu*grad_u + p*I), grad_u_);
auto formP = form1( dx * div_u, p_);
assemble_in_vector(U,formU);
assemble_in_vector(P,formP);
}
auto formUU = form2( dx * nu*_I_, grad_u_);
auto formUP = form2( dx * I, grad_u_, p_);
assemble_in_matrix(U,formUU);
assemble_in_matrix(U,P,formUP,symmetric_counter_part_);
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"X=0"});
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"X=1"});
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Y=0 internal"});
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Y=1 internal"},{sin(_x*pi),Expr(0.)});
}
};
}
void nvi::Stokes_0_grid2(txt output_dir)
{
text name = __FUNCTION__;
using namespace SpaceDiscretisation;
using namespace FormulationFrameworks;
auto processor = Processor__get (name,output_dir);
const bool newton = true;
const uint degreeX = 2;
const uint degreeU = 2;
const int degreeP = -1;
auto pb = UProblem__Stokes__0(processor,name,Mesh(processor,Grid2(50,51,degreeX)),{
.newton = newton,
.degreeU = degreeU,
.degreeP = degreeP,
.nu = 1.
});
if (newton)
{
pb.newton_options.number_of_iterations = 5;
pb.solve();
}
else
{
pb.line_solve(-1);
}
pb.save();
}
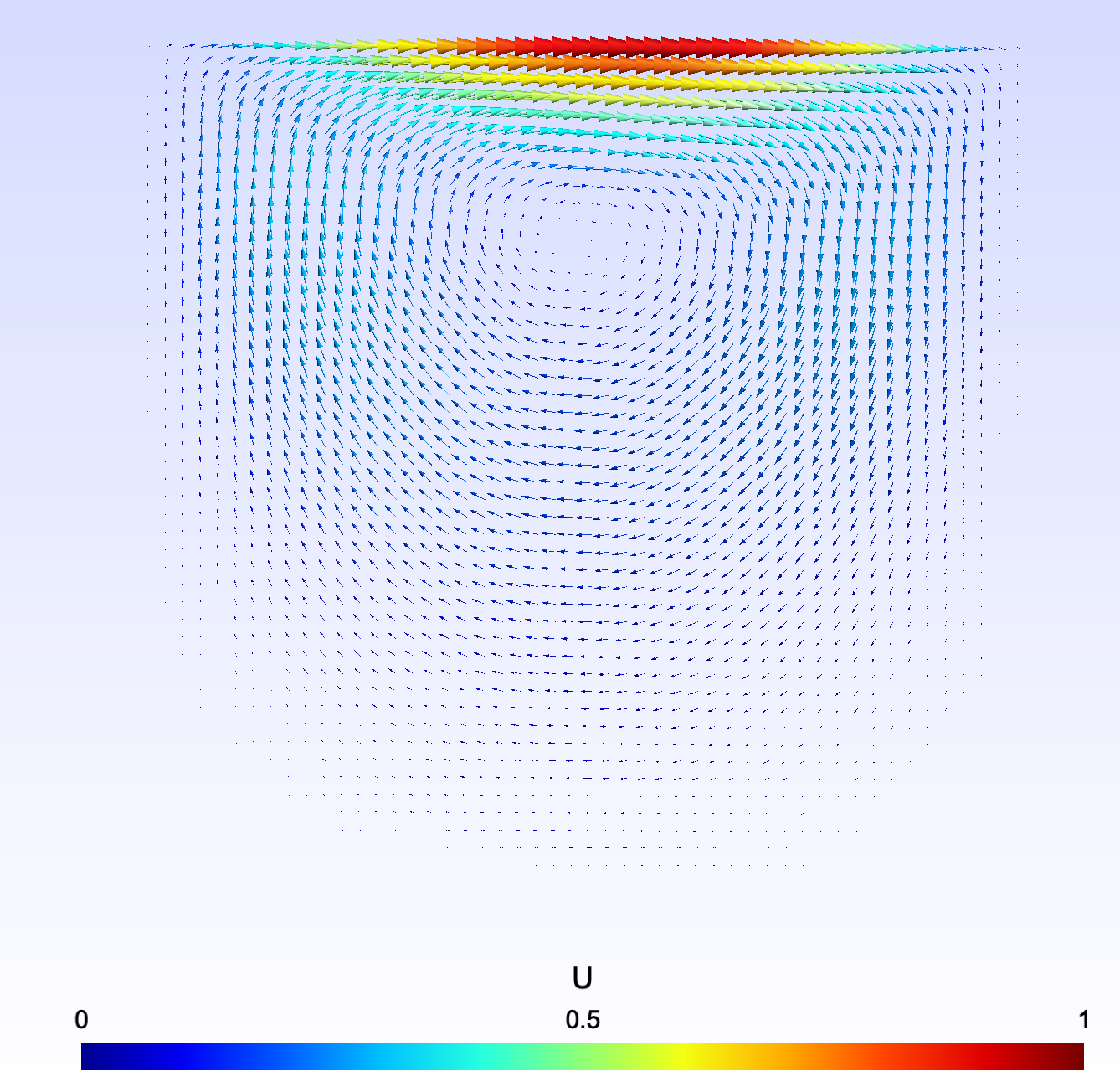
Results
Log file
1 - Creating variable U: [2], degree=2
2 - Creating variable P: [], degree=2
3 - Building
. 1 - Identifying unknown variables
. 2 - Building system
. . 1 - Vector formulations
. . 2 - Vector formulations
. . 3 - Matrix formulations
. . 4 - Matrix formulations
. . 5 - Dirichlet conditions
. . 6 - Dirichlet conditions
. . 7 - Dirichlet conditions
. . 8 - Dirichlet conditions
3 2 * Building system: logs: 0, time: 3.12 ms (cpu: 40 ms)
3 * Building: logs: 0, time: 3.2 ms (cpu: 40 ms)
4 - SparseSystem instantiation
>> symmetry_respect: 1; hermitian_kind 3
$chrono SparseSystem_instantiation: 45 ms (cpu: 540 ms)
5 - Newton initialization
6 - Newton iterations Time[1] = 1
===========================================================
NEWTON : ITERATION 1
===========================================================
|| matrix || = 5.69 619.404
|| rhsU || = 0 0
|| rhsL1 || = 0 0
|| rhsL2 || = 0 0
|| rhsL3 || = 0 0
|| rhsL4 || = 0 0
|| rhsL5 || = 1 7.07107
|| rhsL || = 1 7.07107
|| lhsU || = 1 21.863
|| lhsL1 || = 30.1026 378.52
|| lhsL2 || = 0.25348 0.721822
|| lhsL3 || = 0.430692 1.21561
|| lhsL4 || = 0.0972815 0.715306
|| lhsL5 || = 0.39603 1.24585
|| lhsL || = 30.1026 378.526
---------------- ITERATION 1 TIMES ----------------------
$chrono assembly: 5.18 ms (cpu: 50 ms)
$chrono analysis: 123 ms (cpu: 1.64 s)
$chrono factorisation: 13.4 ms (cpu: 170 ms)
$chrono line_solve: 6.05 ms (cpu: 80 ms)
$chrono Newton iteration: 149 ms (cpu: 1.96 s)
===========================================================
NEWTON : ITERATION 2
===========================================================
|| rhsU || = 1.60288e-14 9.81959e-14
|| rhsL1 || = 7.81194e-16 7.82513e-16
|| rhsL2 || = 5.67512e-21 2.0664e-20
|| rhsL3 || = 7.59224e-21 1.99168e-20
|| rhsL4 || = 5.31928e-21 1.69967e-20
|| rhsL5 || = 7.24798e-21 1.9146e-20
|| rhsL || = 9.81959e-14 7.82513e-16
|| lhsU || = 2.92218e-15 1.13574e-13
|| lhsL1 || = 0.00665125 0.335872
|| lhsL2 || = 8.69444e-05 0.000694223
|| lhsL3 || = 8.69444e-05 0.000694223
|| lhsL4 || = 8.86833e-05 0.0006997
|| lhsL5 || = 8.86833e-05 0.0006997
|| lhsL || = 0.00665125 0.335875
lhsU / lhsU0 = 2.92218e-15
lhsL / lhsL0 = 0.000220953
---------------- ITERATION 2 TIMES ----------------------
$chrono assembly_rhs: 1.35 ms (cpu: 20 ms)
$chrono line_solve: 4.75 ms (cpu: 70 ms)
$chrono Newton iteration: 7.2 ms (cpu: 100 ms)
===========================================================
===========================================================
===========================================================
===========================================================
===========================================================
*** Newton convergence in 2 iterations. STOP. ***
===========================================================
===========================================================
===========================================================
$chrono assembly <mean>: 5.18 ms (cpu: 50 ms)
$chrono assembly_rhs <mean>: 1.35 ms (cpu: 20 ms)
$chrono analysis <mean>: 123 ms (cpu: 1.64 s)
$chrono factorisation <mean>: 13.4 ms (cpu: 170 ms)
$chrono line_solve <mean>: 5.4 ms (cpu: 70 ms)
$chrono update <mean>: 227 us (cpu: 10 ms)
$chrono Newton iteration <mean>: 78 ms (cpu: 1.03 s)
7 - Writing mesh solution: Stokes_0_grid2