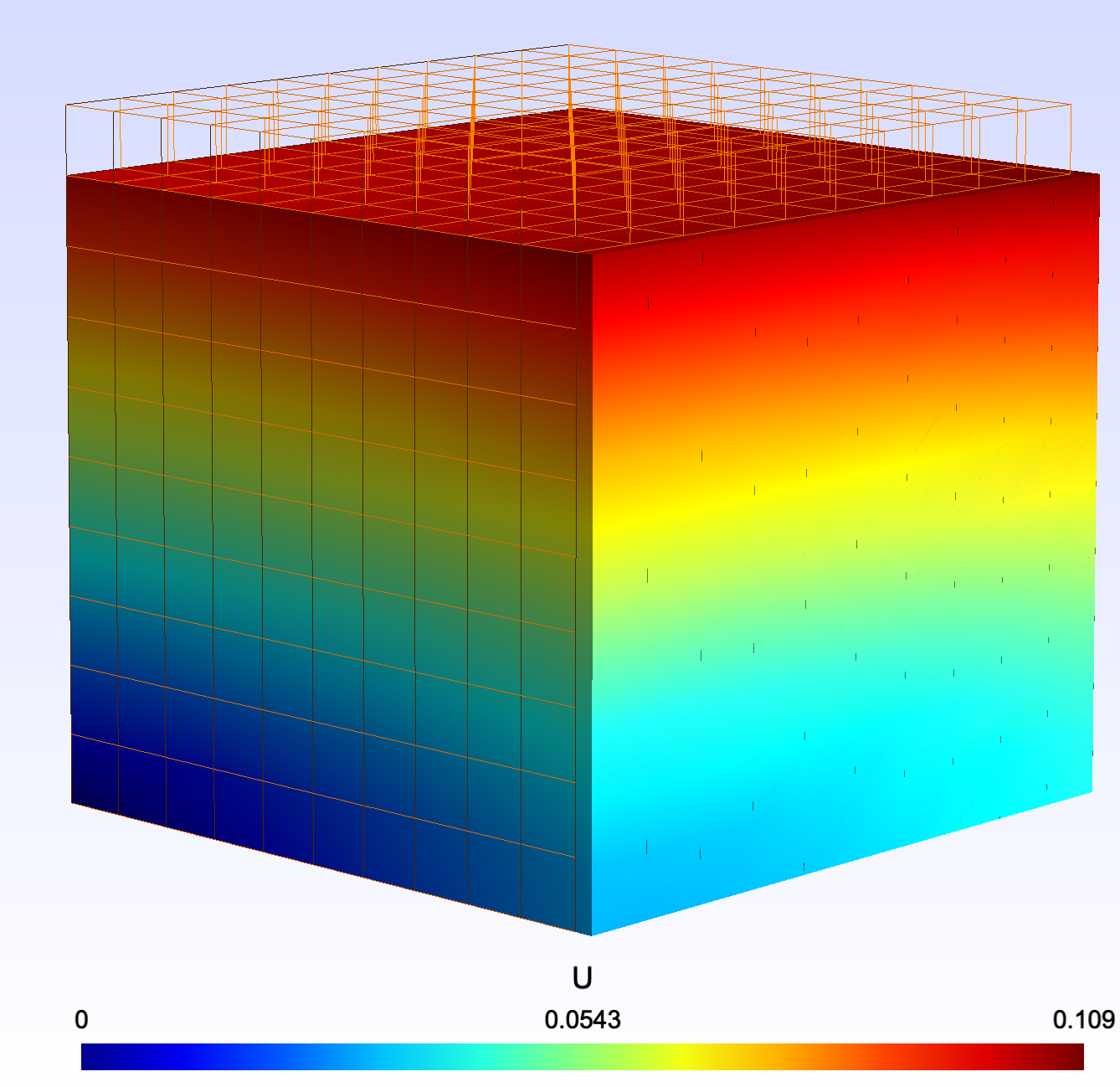
Linear Elasticity
Only the constant stiffness matrix WCC is needed for the formulation.
//
// nvi_LinearElasticity__form__grid3.cpp
// Navpactos-OSX9
//
// Created by Matthieu on 08/10/2014.
// Copyright (c) 2014 Naupacte S.A.R.L. All rights reserved.
//
#include "nvi_LinearElasticity.h"
#include "nvi_Formulation__framework_01.h"
#include "nvi_Material.h"
#include "nvi_Material_FunctionX_Factory.h"
#include <iostream>
namespace nvi::FormulationFrameworks
{
using namespace Material;
struct UProblem__LinearElasticity0 : public Formulation__framework_01
{
UProblem__LinearElasticity0(Processor& p, txt name, Mesh&& m, uint degreeU) : Formulation__framework_01(p,name,std::move(m))
{
auto U = variable("U",3,degreeU);
auto points = _points_ ();
auto dx = _dx_();
auto V = dual(U);
auto Dv = D(V)(points);
// stiffness
auto WCC = WCC__E_nu(1.e5,0.3);
auto formUU = form2(dx*WCC,Dv+transpose(Dv)); // = form2(dx* 4*WCC,Dv)
assemble_in_matrix(U,formUU);
// Imposed dofs
// The bottom nodes remain on their plane
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Z=0"}, 2, 0.);
// The top nodes are imposed a vertical displacement
const double deltaZ = -0.1; // could be an Expr of X.
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Z=1"}, 2, deltaZ);
// Prevent the rigid body motion by blocking node O and keeping node (1,0,0) on its axis
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Origin"}, 0, 0.);
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Origin"}, 1, 0.);
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Axis X end"},1, 0.);
}
};
}
void nvi::LinearElasticity_0(txt output_dir)
{
using namespace SpaceDiscretisation;
using namespace FormulationFrameworks;
text name = __FUNCTION__;
auto processor = Processor__get (name,output_dir);
const uint degreeX = 1;
const uint degreeU = 1;
uint ne1 = 10;
uint ne2 = 10;
uint ne3 = 10;
auto pb = UProblem__LinearElasticity0(processor,name,Mesh(processor,Grid3(ne1,ne2,ne3,degreeX)),degreeU);
pb.line_solve();
pb.save();
}
Linear Elasticity solved as non-linear
We solve the same problem but this time considering it as non-linear. We need to give the formulation of the residual, even it is null. The Newton algorithm shall convice us it is so.
//
// nvi_LinearElasticity__form__grid3.cpp
// Navpactos-OSX9
//
// Created by Matthieu on 08/10/2014.
// Copyright (c) 2014 Naupacte S.A.R.L. All rights reserved.
//
#include "nvi_LinearElasticity.h"
#include "nvi_Formulation__framework_01.h"
#include "nvi_Material.h"
#include "nvi_Material_FunctionX_Factory.h"
#include <iostream>
namespace nvi::FormulationFrameworks
{
using namespace Material;
struct UProblem__LinearElasticity0__as_nonlinear : public Formulation__framework_01
{
UProblem__LinearElasticity0__as_nonlinear(Processor& p, txt name, Mesh&& m, uint degreeU) : Formulation__framework_01(p,name,std::move(m))
{
auto U = variable("U",3,degreeU);
auto points = _points_ ();
auto dx = _dx_();
auto x = X (points);
auto Du = D(U)(points);
auto Id = identity_matrix();
auto materialData = hooke_E_nu(1.e5,0.3); // the coefficients could be expressions (Expr) of X
auto V = dual(U);
auto Dv = D(V)(points);
// C is the linearized strain deformation
auto C = Id+Du+transpose(Du);
// We get the energy, stress, and stiffness
auto [W,WC,WCC] = energyC_tensors(C,materialData);
// Here come the variations of the total energy on the element (Wtot = form0(dx*W))
// formU : elementary vector
// formUU : elementary matrix
auto formU = form1(dx*WC, Dv+transpose(Dv)); // = form1(dx* 2*WC, Dv);
auto formUU = form2(dx*WCC,Dv+transpose(Dv)); // = form2(dx* 4*WCC,Dv);
// Define rhs and matrix
// with the assembly of the elementary vector and matrix using the nodes of U
assemble_in_vector(U,formU); // not necessary as it the problem is linear but allow to check its correctness
assemble_in_matrix(U,formUU);
// Imposed dofs
// The bottom nodes remain on their plane
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Z=0"}, 2, 0.);
// The top nodes are imposed a vertical displacement
const double deltaZ = -0.1; // could be an Expr of X.
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Z=1"}, 2, deltaZ);
// Prevent the rigid body motion by blocking node O and keeping node (1,0,0) on its axis
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Origin"}, 0, 0.);
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Origin"}, 1, 0.);
add_Dirichlet("Dirichlet",U,{"Axis X end"},1, 0.);
}
};
}
void nvi::LinearElasticity0__as_nonlinear(txt output_dir)
{
using namespace SpaceDiscretisation;
using namespace FormulationFrameworks;
text name = __FUNCTION__;
auto processor = Processor__get (name,output_dir);
const uint degreeX = 1;
const uint degreeU = 1;
uint ne1 = 10;
uint ne2 = 10;
uint ne3 = 10;
auto pb = UProblem__LinearElasticity0__as_nonlinear(processor,name,Mesh(processor,Grid3(ne1,ne2,ne3,degreeX)),degreeU);
pb.newton_options.number_of_iterations = 4;
pb.newton_options.eps_r = 1.e-10;
pb.solve();
pb.save();
}
Results